Metabolic Systems Laboratory
The Metabolomic Systems Research Laboratory focuses on studying the crosstalk between metabolism and
epigenetics and how it contributes to changes in cellular systems during mammalian development, germ cell
differentiation such as eggs and sperm, and the occurrence of diseases such as cancer, developmental
abnormalities, and infertility due to abnormalities in these processes.Using human pluripotent stem cells and
human cell culture experimental systems, we establish model platforms for early development, germ cell
development, and cell carcinogenesis. We also aim to establish global evaluation and analysis systems for
metabolic and epigenetic changes. By combining these systems, we comprehensively analyze the behavior of cells
in normal and abnormal states of metabolism and epigenetics in human cells. Additionally, we employ
large-scale genome editing screening technologies to systematically identify the functions of important genes
using these experimental systems.Recent research has revealed morphological and molecular differences between
mammalian animal models and humans during early development. These findings are not only important for zoology
and evolutionary biology but also highlight the indispensability of using human cells for experimental systems
and analyses to understand human biology and for medical applications. Based on our cell analysis technology
platform and establishment of human cell culture model platforms, we aim to generate human cellular models of
related diseases, identify disease markers and therapeutic targets, and apply them to the evaluation of
therapeutic drugs.Our laboratory is interested in application of “imaging metabolomics (IM)” to understanding
pathogenesis of human cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. IM includes imaging mass spectrometry,
surface-enhanced Raman spectrometry (SERS), and ultra-high field functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI).
In November 2023, CIEM introduced 11.7T fMRI.
iMScope
(Imaging mass spectroscopy)

Surface-enhanced Raman
spectroscopy (SERS)
Semiquantitative mass spectrometric images
normal and ischemic murine kidney
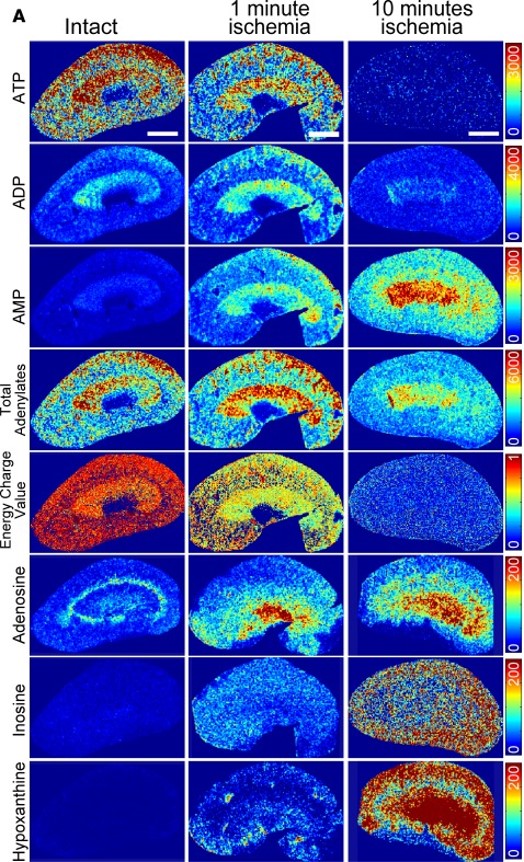
Fujii et al., JCI Insight, 2019
FACSAria III (Cell sorter)

THUNDER Imaging Systems

※References
- DMRT1 regulates human germline commitment
Irie N, Lee S, Lorenzi V, Xu H, Chen J, Inoue M, Kobayashi T, Sancho-Serra C, Drousioti E, Dietmann S, Vento-Tormo R, Song C, Surani A
Nat Cell Biol. 2023 Sep 14.
- The crucial role of muscle
glucocorticoid signaling in accelerating obesity and glucose intolerance via
hyperinsulinemia.
Yamazaki H, Uehara M, Yoshikawa N, Kuribara-Souta A, Yamamoto M, Hirakawa Y, Kabe Y, Suematsu M, Tanaka
H.
JCI Insight. 2023 Apr 24;8(8):e162382.
- Polysulfide Serves as a
Hallmark of Desmoplastic Reaction to Differentially Diagnose Ductal Carcinoma In Situ and Invasive
Breast Cancer by SERS Imaging.
Kubo A, Masugi Y, Hase T, Nagashima K, Kawai Y, Takizawa M, Hishiki T, Shiota M, Wakui M, Kitagawa Y, Kabe
Y, Sakamoto M, Yachie A, Hayashida T, Suematsu M.
Antioxidants. 2023 Jan 20;12(2):240.
- Sensing of the non-essential
amino acid tyrosine governs the response to protein restriction in Drosophila.
Kosakamoto H, Okamoto N, Aikawa H, Sugiura Y, Suematsu M, Niwa R, Miura M, Obata F.
Nat Metab. 2022 Jul;4(7):944-959.
- Cooperative action of
gut-microbiota-accessible carbohydrates improves host metabolic function.
Tomioka S, Seki N, Sugiura Y, Akiyama M, Uchiyama J, Yamaguchi G, Yakabe K, Ejima R, Hattori K, Kimizuka
T, Fujimura Y, Sato H, Gondo M, Ozaki S, Honme Y, Suematsu M, Kimura I, Inohara N, Nunez G, Hase K, Kim
YG.
Cell Rep. 2022 Jul 19; 40(3):111087.
- Omega-3 fatty acid epoxides
produced by PAF-AH2 in mast cells regulate pulmonary vascular remodeling.
Moriyama H, Endo J, Kataoka M, Shimanaka Y, Kono N, Sugiura Y, Goto S, Kitakata H, Hiraide T, Yoshida N,
Isobe S, Yamamoto T, Shirakawa K, Anzai A, Katsumata Y, Suematsu M, Kosaki K, Fukuda K, Arai H, Sano
M.
Nat Commun. 2022 May 31;13(1):3013.
- Sequential enhancer state
remodelling defines human germline competence and specification.
Tang WWC, Castillo-Venzor A, Gruhn WH, Kobayashi T, Penfold CA, Morgan MD, Sun D, Irie N, Surani MA.
Nat Cell Biol. 2022 Apr;24(4):448–460.
- Cancer-derived cholesterol
sulfate is a key mediator to prevent tumor infiltration by effector T cells.
Tatsuguchi T, Uruno T, Sugiura Y, Sakata D, Izumi Y, Sakurai T, Hattori Y, Oki E, Kubota N, Nishimoto K,
Oyama M, Kunimura K, Ohki T, Bamba T, Tahara H, Sakamoto M, Nakamura M, Suematsu M, Fukui Y.
Int Immunol. 2022 Apr 20;34(5):277-289.
- B cell-derived GABA elicits
IL-10+ macrophages to limit anti-tumour immunity.
Zhang B, Volgelzang A, Miyajima M, Sugiura Y, Wu Y, Chamoto K, Nakano R, Hatae R, Menzies RJ, Sonomura K,
Hojo N, Ogawa T, Kobayashi W, Tsutsui Y, Yamamoto S, Maruya M, Narushima S, Suzuki K, Sugiya H, Murakami
K, Hashimoto M, Ueno H, Kobayashi T, Ito K, Hirano T, Shiroguchi K, Matsuda F, Suematsu M, Honjo T,
Faragasan S.
Nature. 2021 Nov;599(7885):471-476.
- On-tissue polysulfide
visualization by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy benefits patients with ovarian cancer to predict
post-operative chemosensitivity.
Honda K, Hishiki T, Yamamoto S, Yamamoto T, Miura N, Kubo A, Itoh M, Chen WY, Takano M, Yoshikawa T,
Kasamatsu T, Sonoda S, Yoshizawa H, Nakamura S, Itai Y, Shiota M, Koike D, Naya M, Hayakawa N, Naito Y,
Matsuura T, Iwaisako K, Masui T, Umemoto S, Nagashima K, Hashimoto Y, Sakuma T, Matsubara O, Huang W, Ida
T, Akaike T, Masugi Y, Sakamoto M, Kato T, Ino Y, Yoshida H, Tsuda H, Hiraoka N, Kabe Y, Suematsu M.
Redox Biol. 2021 May;41:101926.
- Tumors Widely Express
Hundreds of Embryonic Germline Genes.
Bruggeman JW, Irie N, Lodder P, van Pelt AMM, Koster J, Hamer G.
Cancers. 2020 Dec 17;12(12):3812
- Short-chain fatty acids bind
to apoptosis-associated speck-like protein to activate inflammasome complex to prevent Salmonella
infection.
Tsugawa H, Kabe Y, Kanai A, Sugiura Y, Hida S, Taniguchi S, Takahashi T, Matsui H, Yasukawa Z, Itou H,
Takubo K, Suzuki H, Honda K, Handa H, Suematsu M.
PLoS Biol. 2020 Sep 29;18(9):e3000813.
- A Flexible, Pooled CRISPR
Library for Drug Development Screens.
Blanck M, Budnik-Zawilska MB, Lenger SR, McGonigle JE, Martin GRA, le Sage C, Lawo S, Pemberton HN, Tiwana
GS, Sorrell DA, Cross BCS.
CRISPR J. 2020 Jun;3(3):211-222.
- A PAX5-OCT4-PRDM1
developmental switch specifies human primordial germ cells.
Fang F, Angulo B, Xia N, Sukhwani M, Wang Z, Carey CC, Mazurie A, Cui J, Wilkinson R, Wiedenheft B, Irie
N, Surani MA, Orwig KE, Reijo Pera RA.
Nat Cell Biol. 2018 Jun;20(6):655-665.
- Segregation of mitochondrial
DNA heteroplasmy through a developmental genetic bottleneck in human embryos.
Floros VI, Pyle A, Dietmann S, Wei W, Tang WCW, Irie N, Payne B, Capalbo A, Noli L, Coxhead J, Hudson G,
Crosier M, Strahl H, Khalaf Y, Saitou M, Ilic D, Surani MA, Chinnery PF.
Nat Cell Biol. 2018 Feb; 20(2):144-151.
- What Can Stem Cell Models
Tell Us About Human Germ Cell Biology?
Irie N, Sybirna A, Surani MA.
Curr Top Dev Biol. 2018;129:25-65.
- Dual direction CRISPR
transcriptional regulation screening uncovers gene networks driving drug resistance.
le Sage C, Lawo S, Panicker P, Scales TME, Rahman SA, Little AS, McCarthy NJ, Moore JD, Cross BCS.
Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 18;7(1):17693.
- Principles of early human
development and germ cell program from conserved model systems.
Kobayashi T, Zhang H, Tang WWC, Irie N, Withey S, Klisch D, Sybirna A, Dietmann S, Contreras DA, Webb R,
Allegrucci C, Alberio R, Surani MA.
Nature. 2017 Jun 15;546(7658):416-420.
- Germline competency of human
embryonic stem cells depends on eomesodermin.
Chen D, Liu W, Lukianchikov A, Hancock GV, Zimmerman J, Lowe MG, Kim R, Galic Z, Irie N, Surani MA,
Jacobsen SE, Clark AT.
Biology of Reproduction. 2017 Jan 1;97(6):850-861.
- Efficient Induction and
Isolation of Human Primordial Germ Cell-Like Cells from Competent Human Pluripotent Stem
Cells.
Irie N, Surani MA.
Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1463:217-226.
- Specification and epigenetic
programming of the human germ line.
Tang WWC, Kobayashi T, Irie N, Dietmann S, Surani MA.
Nat Rev Genet. 2016 Oct;17(10):585-600.
- CRISPR-Cas9(D10A)
nickase-based genotypic and phenotypic screening to enhance genome editing.
Chiang TW, le Sage C, Larrieu D, Demir M, Jackson SP.
Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 15;6:24356.
- Human Germline Development from
Pluripotent Stem Cells in vitro.
Irie N, Kim S, Surani MA.
Journal of Mammalian Ova Research. 2016;33(2):79-87.
- SOX17 is a critical
specifier of human primordial germ cell fate.
Irie N, Weinberger L, Tang WWC, Kobayashi T, Viukov S, Manor YS, Dietmann S, Hanna JH, Surani MA.
Cell. 2015 Jan 15;160(1-2):253-68.
- A Unique Gene Regulatory
Network Resets the Human Germline Epigenome for Development.
Tang WWC, Dietmann S, Irie N, Leitch HG, Floros VI, Bradshaw CR, Hackett JA, Chinnery PF, Surani MA.
Cell. 2015 Jun 4;161(6):1453-67.
- Effective expansion of
engrafted human hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow of mice expressing human
Jagged1.
Negishi N, Suzuki D, Ito R, Irie N, Matsuo K, Yahata T, Nagano K, Aoki K, Ohya K, Hozumi K, Ando K,
Tamaoki N, Ito M, Habu S.
Exp Hematol. 2014 Jun;42(6):487-94.e1.
- Germ cell specification and
pluripotency in mammals: a perspective from early embryogenesis.
Irie N, Tang WWC, Surani MA.
Reprod Med Biol. 2014;13(4):203-215.
- Perceiving signals, building
networks, reprogramming germ cell fate.
Barrios F, Irie N, Surani MA.
The International journal of developmental biology. 2013;57(2-4):123-32.
- Osteosclerosis and
inhibition of human hematopoiesis in NOG mice expressing human Delta-like 1 in
osteoblasts.
Ito R, Negishi N, Irie N, Matsuo K, Suzuki D, Katano I, Hayakawa E, Kawai K, Kamisako T, Eto T, Ogura T,
Hozumi K, Ando K, Aiso S, Tamaoki N, Habu S, Ito M.
Exp Hematol. 2012 Nov;40(11):953-963.e3.
- Bidirectional signaling
through ephrinA2-EphA2 enhances osteoclastogenesis and suppresses osteoblastogenesis.
Irie N, Takada Y, Watanabe Y, Matsuzaki Y, Naruse C, Asano M, Iwakura Y, Suda T, Matsuo K.
J Biol Chem. 2009 May 22;284(21):14637-44.
- Osteoclast-osteoblast
communication.
Matsuo K, Irie N.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008 May 15;473(2):201-9.
- Bidirectional ephrinB2-EphB4
signaling controls bone homeostasis.
Zhao C, Irie N, Takada Y, Shimoda K, Miyamoto T, Nishiwaki T, Suda T, Matsuo K.
Cell Metabolism. 2006 Aug;4(2):111-12.
- Transcription factors in
osteoclast differentiation.
Matsuo K, Irie N.
Nippon Rinsho. 2005 Sep;63(9):1541-6.




